Our paper titled “Uncovering optimal carbon and boron nitride nanotube geometries for methane and hydrogen release” has been published online in the journal “International Journal of Hydrogen Energy”, accessible at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.07.025
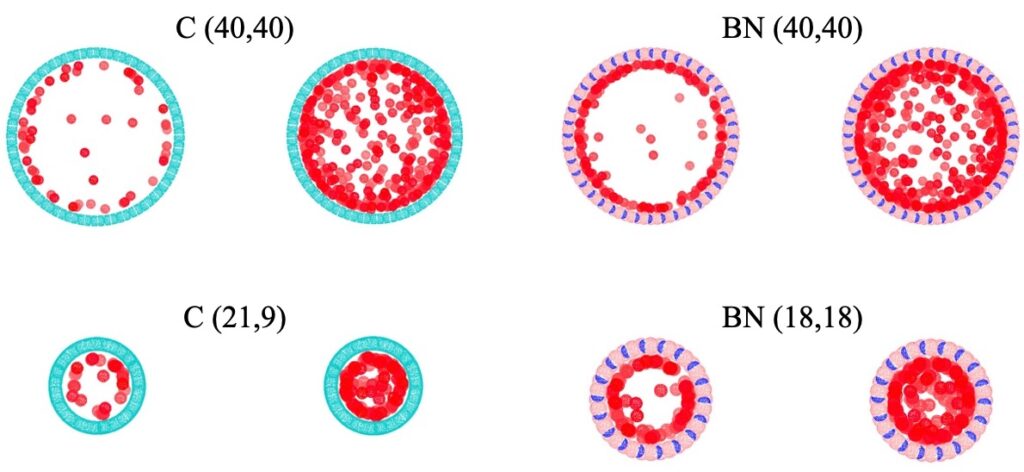
Through GCMC simulations of 1651 carbon and BN nanotubes, we explored CH4 and H2 release at 298 K and 77 K, revealing that while specific nanotubes like C(40,40) and BN(40,40) for CH4 and C(40,39) and BN(40,40) for H2 show high release capacities, they do not meet DOE targets. Notably, H2 release in the C(28,7) nanotube approaches the DOE volumetric target at a 1 nm van der Waals spacing. The study emphasizes the importance of extra-tube adsorption, which contributes significantly to the overall gas storage capacity. These findings are instrumental for designing nanotube-based materials for efficient gas storage, with significant implications for clean energy applications.
“The International Journal of Hydrogen Energy” serves as a key forum for scientists and engineers globally to share and disseminate innovative ideas, technological advancements, and research findings in hydrogen energy. The journal focuses on original analytical and experimental studies encompassing hydrogen production, storage, transportation, applications, supportive technologies, environmental effects, and the economic and global dimensions of hydrogen and related energy carriers like ammonia, methane, and alcohols.
The journal is classified as Q1 in the latest edition of the Web of Science (WOS) journal ranking. The 2024 impact factor is 8.1, with a CiteScore of 13.50 and an SJR (Scientific Journal Ranking) index of 1.513. The Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) SCI Journal Ranking (Engineering and Technology, Zone 2).